Pseudocyesis / False Pregnancy
Written by Dr.M.D.Mazumdar, MD
Pseudocyesis or 'false pregnancy' or 'phantom pregnancy' is a condition in which a woman believes that she is pregnant and even gets all the symptoms_of_pregnancy such as missed periods, weight gain, morning sickness, and even lactation. The only thing missing is the baby.
What is Pseudocyesis?
Studies have shown that Pseudocyesis is a psychosomatic conditions. A psychosomatic condition is one in which there is the occurrence of physical symptoms withough any medical cause but due too an underying psychological cause.
Pseudocyesis occurs when a woman is either desperate for a child or overcome with fears that she is pregnant. It is the result of a delicate mind-body relationship and is proof of the degree to which the mind is able to control the body.

Pseudocyesis
An intense desire for a child, or a deep depression triggers the pituitary gland into producing elevated hormones which mimic the hormone changes of real pregnancy.
The first written account of a false pregnancy was given by Hippocrates in 300 BC. The most famous case of phantom pregnancy was that of Queen Mary 1 of England who claimed to be pregnant for 11 months before it was diagnosed that she was not pregnant.
It affects all ethnic, racial, and socioeconomic groups. It is most common in women aged 20 to 39 years, but has been described in premenarchal and postmenopausal women. False pregnancy was more common before reliable pregnancy tests like ultrasounds were invented.
Some men experience a related phenomenon known as couvade, or sympathetic pregnancy. They will develop many of the same symptoms as their pregnant partners, including weight gain, nausea, and backache.
Incidence rates of pseudocyesis range from 1 to 6 per 22,000 births.
What is the cause of Pseudocyesis? Are some women more at risk for developing Pseudocyesis
Pseudocyesis can occur in all women but some women are more at risk:
- Women with infertility who have been trying for a child for a long time.
- Women who have recently suffered an abortion or miscarriage.
- Women who are afraid of an unwanted pregnancy, for example, a rape victim.
- Women who have suffered an incestuous relationship.
- Women with a deep depression who tend to convert their mental trauma into the physical symptoms of pregnancy.
- Women who have a history of experiencing symptoms of pregnancy in the past, such as morning sickness or lactation.
- Women with hormonal imbalances and irregular periods.
- Women who have underlying psychological problems
- Women who experience high levels of stress, especially those who are under family or society pressures to get pregnant.
- Women with particular illnesses which cause irregular or delayed periods, such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid issues, and metabolic issues.
- Women with conditions like tumors of the uterus or ovaries or premature menopause.
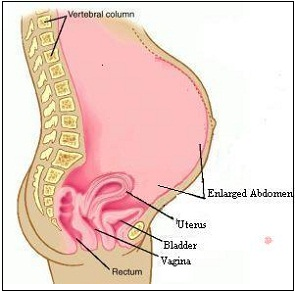
Pseudocyesis
Symptoms of Pseudocyesis
The symptoms of pseudocyesis are the same as the symptoms of normal pregnancy.
Some women however manage to suppress their periods completely so that they do not get any bleeding at all during the false pregnancy.
Enlargement of the abdomen occurs due to the accumulation of increased amounts of gas and fat in the abdomen. The intestinal loops become grossly distended with gas while fat is accumulated in the layers of the abdominal wall as well as inside the abdomen.
Some of the increased size of the abdomen is also due to an increased curvature of the lower back, pushing the abdomen forwards.
The enlarged abdomen deflates suddenly when the woman is put under anesthesia.
Prolactin, together with increasing levels of progesterone and estrogen causes enlargement of the breast tissue, as well as secretion of breastmilk.
Some amount of muscle twitching can also occur which can also be mistaken for fetal movement.
Difference between a true pregnancy and Pseudocyesis
The similarities and differences are laid down in the table below:
| True Pregnancy | Pseudocyesis | |
| Loss of Periods | Present | Present/Spotting in some cases |
| Enlarging Abdomen | Present | Present |
| Morning Sickness | Present | Present |
| Breast enlargement | Present | Present |
| Fetal Movement | Present | Apparently Present |
| Pregnancy Test | Positive | Negative |
| Ultrasound | Fetus present | Fetus Absent |
Diagnosis of Pseudocyesis
Since the symptoms of Pseudocyesis are the same as a normal pregnancy, it can be difficult to diagnose based on the patient's symptoms alone. It needs to be diagnosed by careful physical examinaiton, blood tests and ultrasound. It is is diagnosed by:
- Pelvic examination: A pelvic examination will reveal a normal sized uterus even in later pregnancy. There will not be a gradual increase in the size of the uterus as seen in a normal pregnancy. No fetus can be felt.
- Urine Tests :The urine test, even the morning urine test for pregnancy, will be negative.
- Blood tests: Blood tests, for beta human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) test, can be done to check for the presence of pregnancy hormones. The test is always negative, although a false positive test is sometimes seen.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound is usually the most accurate and final diagnosis. No fetus is seen at any time during the so-called pregnancy.
- Psychological evaluation: The patient should undergo tests and examination to to pinpoint any underlying psychological problems that might be causing the condition. A psychological evaluation may be necessary.
The main diagnostic points are:
Treatment of Pseudocyesis
The main treatment of pseudocyesis is by psychotherapy. Most women can be convinced that they are not pregnant by showing them the ultrasound reports. But the underlying psychological problems need to be analysed and treated by a psychiatrist.
- Counseling or therapy: Counseling or therapy may be helpful for a woman with pseudocyesis to help her deal with the psychological and emotional effects of the disorder. This includes dealing with any underlying emotional problems that might have contributed to the development of pseudocyesis.
- Hormonal therapy: Hormonal therapy may be used to manage any hormonal imbalabces that might be causing the symptoms.
- Medicines: Medicines may be needed to control specific symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting.
- Supportive care: A woman with pseudocyesis needs good supportive care, from her family as well as by medical professionals. It must be understood that she is suffering from a psychological issue and needs empathy and understanding. Regular check-ups and follow-up appointments to monitor her physical and emotional well-being are needed.
Can Pseudocyesis be prevented?
Prevention of Pseudocyesis is difficult since it is difficult to know whta triggers it. But certain steps may be taken in women who are at risk:
- Stress: Women who are under stress should be carefully monitored, especially if the stress is about fertility issues, marital problems and rape or sexual problems.
- Psychological Sress: Women who suffer from depression and anxiety should undergo treatment and counselling.
- Family Support: Family support is vital. It will help her cope with these difficult experiences and reduce stress and depression.
- Regular check-ups and follow-up appointments: Keeping regular check-ups with a doctor can help identify any potential issues early on and prevent them from developing into more serious conditions.
Read More:
Also Read-
- How Pregnancy Occurs.
- The Normal Menstrual Cycle.
- Vaginal Discharge with Itching .
- Causes and Treatment of Sexuallly Transmiited Diseases.
Do you have a gynecological or obstetrical problem? Would you like to discuss it in private? Consult our online gynecologist Dr.M.D.Mazumdar, MD (O&G), at any time you want and get your reply within 24 hours.We charge a nominal fee of USD 20 ($20) per question through Paypal.com.
The procedure of asking a question is quite simple. Clicking on the link below takes you to the Paypal website where the payment is made. After the payment goes through, you will be directed back to this website where you can ask your question. And rest assured, you will get your answer within 24 hours. And usually, even sooner.