Asherman's Syndrome
Written by Dr.M.D.Mazumdar, MD
Asherman's Syndrome is an uncommon condition of the uterus in which there is formation of scar tissue (called 'adhesions' or 'synechia') inside the uterine cavity. These synechia obliterates the endometrial cavity partially or completely and prevents the occurance of normal menstrual periods.
The normal anatomy of the uterus consists of two thick muscular walls (the anterior uterine wall and the posterior uterine wall) enclosing a cavity called the endometrial cavity. The tissue lining of this cavity is called the 'endometrium'.
The main function of the endometrium is to proliferate and change in structure during each menstrual cycle so that a fertilized ovum can implant in it, should pregnancy occur in that cycle. If pregnancy does not occur, the endometrium degenerates and sloughs off during the menstrual period.
Adhesions inside the uterus can damage the endometrium to a greater or lesser degree. It thus fails to develop in each menstrual cycle leading to secondary amenorrhea.
Asherman's syndrome can occur in any women of any age who have undergone an intra-uterine procedure like an abortion, D&C or a childbirth. But it is most common after a D&C is performed on a recently pregnant uterus. It is the result of vigorous scraping resulting in damage to the basal layer of the endometrium.
Adhesions inside the uterus is sometimes deliberately caused to decrease the size and thickness of the endometrium in women who have excessive bleeding. It helps to stop the periods and prevent surgeries like a hysterectomy. It can be done by endometrial ablation with a laser, or electocautery or hydrothermal balloons. This is an artificial scarring of the endometrium and is not included under Asherman's syndrome.

Asherman's Syndrome
Grades of Asherman's Syndrome
Depending on the extent and thickness of the adhesions, Asherman's Syndrome can be graded into mild, moderate or severe.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
Causes of Asherman's Syndrome
The basic cause of Asherman's syndrome is injury to the endometrium, causing formation of scar tissue between the two uterine walls.

Pathophysiology of Asherman's Syndrome
Symptoms
The symptoms of Asherman's Syndrome can vary, depending on its severity. Mild Asherman's may not cause any symptoms at all. Some of the most common signs and symptoms include:
- Heavy or light menstrual periods or complete absence of menstrual bleeding
- Painful menstrual periods
- Pain and/or cramping during intercourse
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Low back pain
- Lower abdominal pain
- Passing of white and/or clear discharge
- Abnormal bleeding or spotting between menstrual periods
- Infertility
- Recurrent miscarriages.
Diagnosis
Asherman's syndrome is not easy to diagnose by by physical signs and symptoms alone. A mild case may not have any symptoms. Diagnostic measures like ultrasounds are necessary for a accurate diagnosis.
- Ultrasound - Ultrasound is one of the most commonly used diagnostic aid. A very thin endometrial lining in a patient with amenorrhea (loss of periods), or other menstrual irregularities may be suggestive of adhesive scarring inside the uterus. Some areas in the endometrium may be thin due to the scars and lack of growth of the endometrium .
- Blood Tests - Blood tests may be need to be ordered to rule out infections, especially infections with Chlamydia or Tuberculosis.
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG) - HSG is a procedure in which a radio-opaque dye is injected into the uterus by a special canula. The movement of the dye is tracked by a series of Xrays. Any defect in the endometrium or adhesions may show up as deficient space occupying spots .
- Saline sonography - Saline sonography is similar to HSG except that it uses saline instead of dye for the diagnosis. Advantages of saline sonography compared with hysterosalpingography are that it does not involve radiation or a special diagnosis suite. It can be done in the office.
- Hysteroscopy - A hysteroscopy is can usually confirm the diagnosis. A hysteroscope is a slender tube through which a camera can be inserted into the vagina and uterus to examine the inner cavity of the uterus under direct vision. Hysteroscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing, classifying and treating the disease. Diagnosis with hysteroscopy may be combined with treatment procedures like lysis of the scar tissue.
Treatment
Asherman's syndrome is treated using a combination of medicinal and surgical techniques. The main aims of treatment are (1) Removal of the scars and (2) Encourage growth of nomal endometrium.
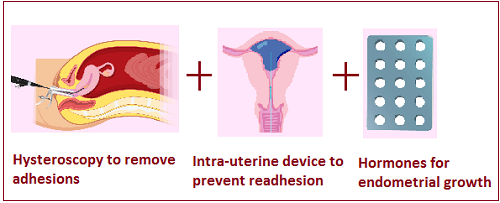
Treatment of Asherman's Syndrome
The two uterine walls should be held apart as far as possible during the healing process to prevent recurrance of adhesions. This is usually done by inserting an intrauterine device (IUCD) like Cu-T or Lippes loop or a balloon stent (Foley catheter or Cook stent) containing saline for up to 3 weeks immediately after the adhesions are removed.
Prevention
Asherman's syndrome can be prevented by avoiding surgery on the uterus as far as possible.
- Medical alternatives to D&C for evacuation of retained placenta/products of conception, medicines like misoprostol, methotrexate and mifepristone should be used. This can help prevent a D and C. Studies show that this less invasive and cheaper method to be to be efficacious, safe and an acceptable alternative to surgical management for most women.
Alternatively, D&C could be performed under ultrasound guidance rather than as a blind procedure . The surgeon would be able to stop scraping the lining once all residual tissue has been eliminated, avoiding an injury to the endometrium.
- Infections Treatment of infections very early may help prevent adhesions
- Miscarriages Miscarriages can be treated by a combination of Misoprostol to evacuate the uterus and antibiotics to prevent an infection.
Read More:
Also Read-
- Interesting Facts about the Period.
- The Female Reproductive Organs.
- Vaginal Discharge with Itching .
- Causes of Male and Female Infertility.
Do you have a gynecological or obstetrical problem? Would you like to discuss it in private? Consult our online gynecologist Dr.M.D.Mazumdar, MD (O&G), at any time you want and get your reply within 24 hours.We charge a nominal fee of USD 20 ($20) per question through Paypal.com.
The procedure of asking a question is quite simple. Clicking on the link below takes you to the Paypal website where the payment is made. After the payment goes through, you will be directed back to this website where you can ask your question. And rest assured, you will get your answer within 24 hours. And usually, even sooner.